
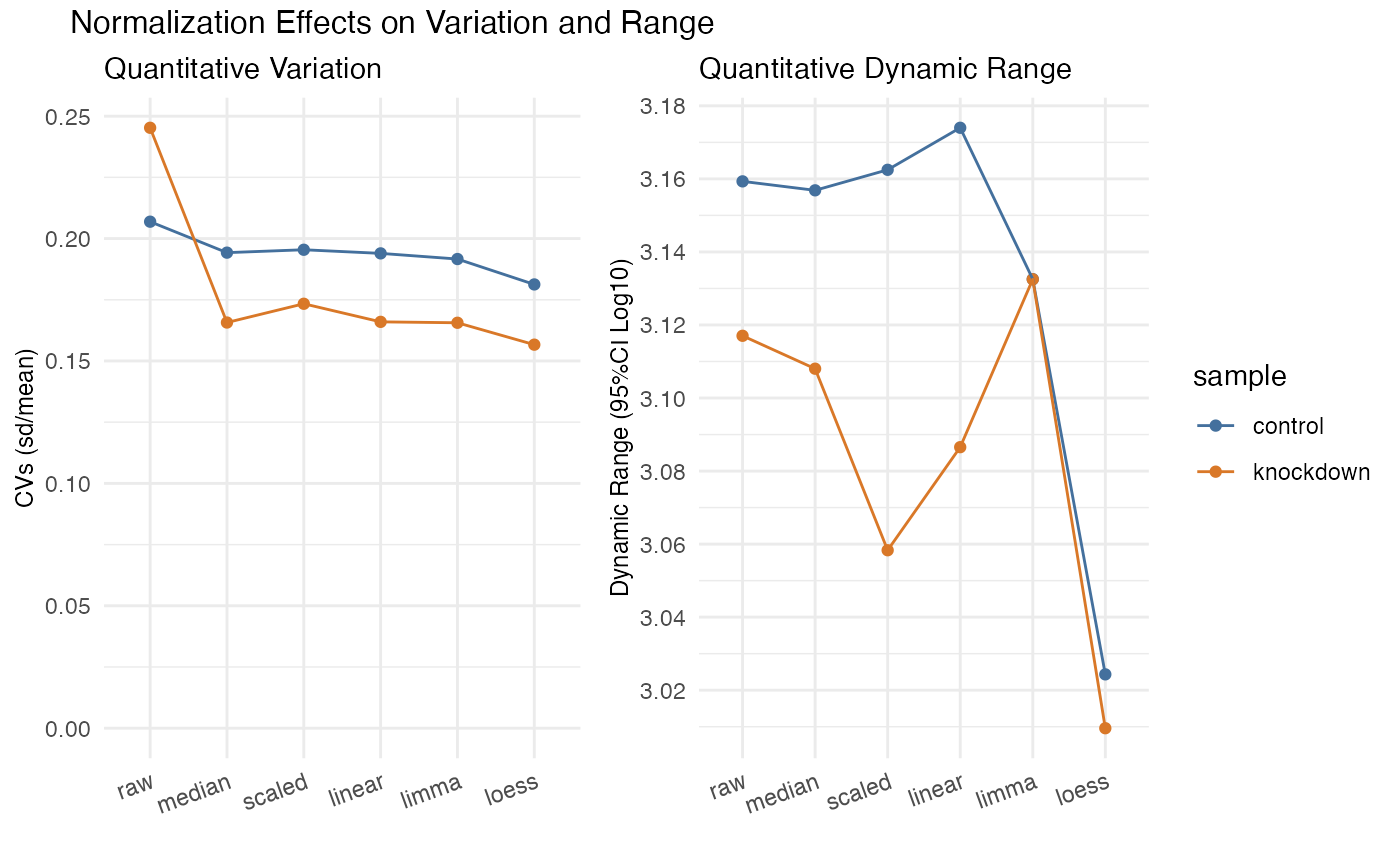
Plot the variation in normalized values
plot_variation_cv.Rdplot_variation_cv() is a GGplot2 implementation for plotting the variability in
normalized values, generating two facets. The left facet is a plot of CVs for
each normalization method. The right facet is a plot of the 95%CI in abundance,
essentially the conservative dynamic range. The goal is to select a normalization
method that minimizes CVs while also retaining the dynamic range.
Examples
library(dplyr, warn.conflicts = FALSE)
library(tidyproteomics)
hela_proteins %>%
normalize(.method = c("scaled", "median", "linear", "limma", "loess")) %>%
plot_variation_cv()
#> ℹ Normalizing quantitative data
#> ℹ ... using scaled shift
#> ✔ ... using scaled shift [160ms]
#>
#> ℹ ... using median shift
#> ✔ ... using median shift [140ms]
#>
#> ℹ ... using linear regression
#> ✔ ... using linear regression [227ms]
#>
#> ℹ ... using limma regression
#> ✔ ... using limma regression [394ms]
#>
#> ℹ ... using loess regression
#> ✔ ... using loess regression [1.3s]
#>
#> ℹ Selecting best normalization method
#> ✔ Selecting best normalization method ... done
#>
#> ℹ ... selected loess
 #> TableGrob (2 x 2) "arrange": 3 grobs
#> z cells name grob
#> 1 1 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
#> 2 2 (2-2,2-2) arrange gtable[layout]
#> 3 3 (1-1,1-2) arrange text[GRID.text.5457]
#> TableGrob (2 x 2) "arrange": 3 grobs
#> z cells name grob
#> 1 1 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
#> 2 2 (2-2,2-2) arrange gtable[layout]
#> 3 3 (1-1,1-2) arrange text[GRID.text.5457]